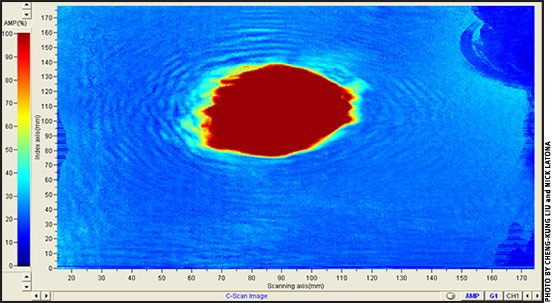
An ultrasound image of a steer hide reveals a defect (red area).
Detecting Defects Hidden in Hides
Ultrasonic waves provide means of detecting defects, assessing quality.
An Agricultural Research Service (ARS) scientist has found a way to find hidden defects in the animal hides that become our footwear, sporting goods, fashion accessories and other leather goods.
About 90% of the 32 million hides produced by the meat industry in the United States each year are exported. Before they are sold in international markets, they are visually inspected, weighed and given a numeric grade. Many hides, however, have hidden defects caused by insect bites, abrasions, scars and natural rough spots.
Processing and selling animal hides is a $2-billion industry in the United States, and the lack of any technology for measuring defects and characterizing quality often leads to disputes after the hides are sold, states Stephen Sothmann, president of the U.S. Hide, Skin and Leather Association, which represents leather goods manufacturers and meatpackers, processors and traders who export hides.
Cheng-Kung Liu, an ARS materials engineer in Wyndmoor, Pa., may have found a solution: The use of ultrasonic waves.
Ultrasonic waves are sound waves. When they are transmitted through an object, defects or rough spots on the object’s surface — even those that can’t be seen by the naked eye — will change the intensity of the signal. Ultrasonic waves are now used to grade lumber and to identify defects on aircraft parts, NASA technology and the surfaces of other precision materials, according to Liu.
Liu scanned hides by sending low-frequency airborne ultrasonic (AU) signals through the hides to a receiver a few centimeters away. He collected enough data to accurately assess defects and to predict the potential quality of the leather’s toughness, strength, stiffness and other factors. The scans also did not cause any damage.
Because the equipment is based on commercially available technologies, Liu anticipates having a scanner available for industrial use in two to three years.

Editor’s Note: Read more about this research in the August 2017 issue of AgResearch magazine. The Agricultural Research Service is the USDA’s chief scientific in-house research agency.






