Finding Fevers From the Air
AgriLife Research targets feverish cows with drones.

Scientists within The Texas A&M University System are testing new technologies at a feedlot in the Texas Panhandle to find ways to reduce the use of antibiotics in livestock and provide consumers with a healthy meat supply.
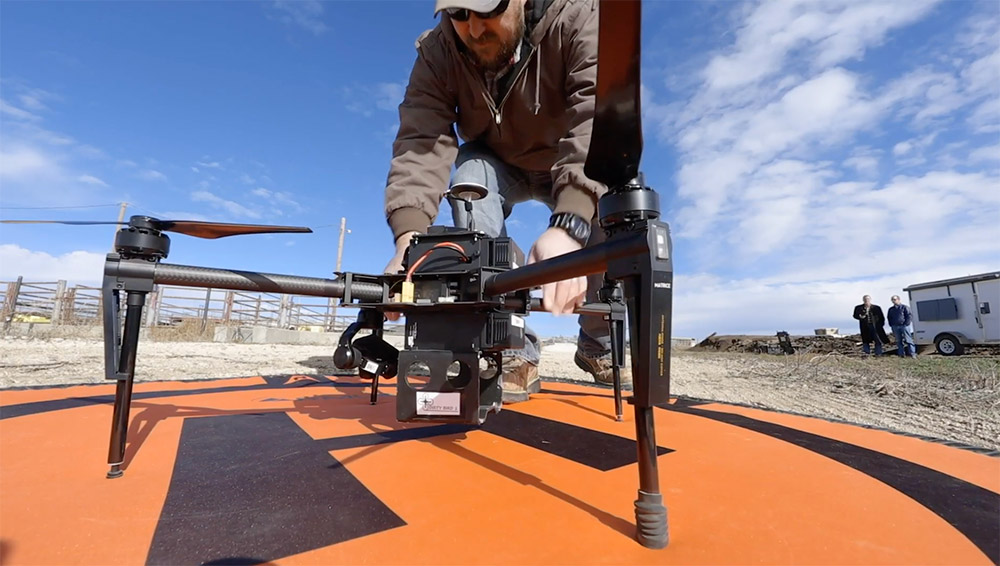
Lately, drones equipped with thermal imaging cameras have been buzzing over a research feedlot near Amarillo, as researchers develop test methods to identify feverish animals before they show symptoms of illness, such as eating less feed, or infect other animals.
Engineers from Texas A&M AgriLife Research believe that producers will be able to detect sick animals earlier and target their use of antibiotics more precisely than is possible with current technology.
Small, remote-controlled and unmanned aerial vehicles are already central to a type of technology-assisted farming known as “precision agriculture.” Drones have been used to monitor crops to help reduce water, fertilizers and pesticides.
Now their use is being explored with livestock. It is a natural extension of precision agriculture, Texas A&M University System Chancellor John Sharp said.
“Millennials are getting blamed all the time for destroying industries, but in this case, they are creating one,” Sharp said. “Demand for antibiotic-free meat and ingenuity from Texas A&M AgriLife Research scientists is leading to some very exciting technology and a new segment of precision agriculture.”
 |
Drones equipped with thermal imaging cameras have been buzzing over a research feedlot near Amarillo, as researchers develop test methods to identify feverish animals before they show symptoms of illness. [Photos courtesy Texas A&M AgriLife Research] |
Brent Auvermann, center director at Texas A&M AgriLife Research and Extension Center in Amarillo, said drones are being used more than ever nowadays to address issues of modern life.
“By taking images and using sensors of different kinds from above, we think we’ll be able to tell what needs to be done and go do it,” he said.
The use of drones to pick out sick cattle isn’t AgriLife Research’s only way to spot sick livestock. Scientists in College Station and the Panhandle also are experimenting with video cameras and artificial intelligence to identify ailing animals based on their behavior.
“Veterinarians already use thermal imaging in their clinical practice, for example, to detect lameness in horses,” Auvermann said. “We’re thinking we ought to be able to put a thermography instrument up in the air and extend its usefulness, especially as the technology gets better and cheaper.”
To watch a video on this technology, visit https://youtu.be/tWVxOuLwsv4.
Editor’s note: Blair Fannin is a media relation specialist with Texas AgriLife Extension Communications.