When is the Best Time
to Spread Manure?
MSU EnviroImpact is a new tool for Michigan livestock producers to use when deciding on manure applications.
When is the best time to spread manure for optimal crop production and minimize environmental losses? The simple answer is it depends on many factors. While not exactly a satisfying answer to a complex scenario, it truly depends on the manure handling system, cropping system, field conditions, weather forecasts, time and labor available, volume of manure in the pit, and many more factors. What is the right decision when there are so many factors out of our control? The best answer is to know the risk factors during the time of manure application and minimize those risks while optimizing crop production with those additional manure nutrients.
Manure injection equipment used on a farm field.
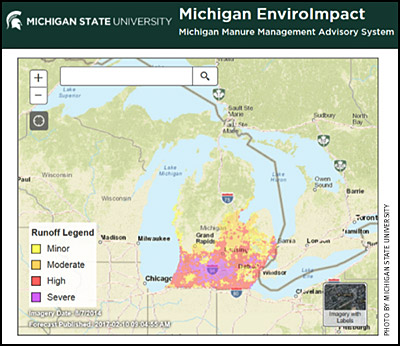
The MSU EnviroImpact Tool provides maps showing short-term runoff risks for daily manure application planning purposes; taking into account factors including precipitation, temperature, soil moisture and landscape characteristics. Anyone handling and applying livestock manure in Michigan can use this tool to determine how risky it will be to spread manure on their fields.
Key features of this tool include:
- Ability to sign up for email or text message alerts specific to your field locations for high-risk runoff days.
- Easy visualization of the short-term risk of manure runoff (Fig. 1).
- Ability to zoom in on the map to your field(s) and click on the location to determine the potential risk of runoff from manure application.
- Capability to login to the tool to draw and save your fields on the map to determine risk of runoff at any time.
- Automatic daily runoff risk forecast updates from the National Weather Service.
- Access to additional resources on manure management.
While the purpose of these maps is to help reduce the risk of applied manure leaving the fields, it is very important to follow your farm’s manure management plan and to assess the risk for each field prior to manure applications. Always apply your own knowledge of your fields and landscapes when assessing the risk of runoff from manure applications. Remember this tool is just one of many in your own toolbox.
Additional manure application considerations
Risk increases with soil moisture. If you know that your fields are particularly wet, you should know that the risk of runoff from your fields would be higher than what is shown on the risk map. The opposite may hold true if you estimate that your soil moisture values are lower.
Even if the map shows low risk of runoff, your fields may not be dry enough to spread manure. Applying liquid manure [typically equivalent to ⅓ to 1 inch (in.) or more of rainfall] to wet fields could lead to a direct manure runoff, even if the field is otherwise a low risk site due to low slope, etc. Make sure your fields are dry enough to accept additional moisture. Additionally, operating field equipment on wet fields could lead to soil compaction.
Liquid manure applications increase soil moisture. An application of 27,000 gallons per acre of liquid manure is the equivalent of adding approximately 1 in. of water to your fields. A liquid manure application effectively increases your soil moisture, and therefore the risk of runoff from fields receiving liquid manure could be higher than what is shown on the risk map.
Snow-covered and frozen fields are high-risk. If you have snow on your fields, the risk of runoff from your fields could be higher, especially if spreading manure in the later winter months of February or March (due to snowmelt or rainfall).
Some fields are always higher-risk areas. These are areas of concern on your farm and might include fields with higher slopes, tighter soils (clay), poor drainage or close to sensitive areas such as surface waters, etc. Many of these areas should be identified in your manure management plan and/or sensitive area maps. Use caution when applying manure in these areas, regardless of what the risk map indicates.
Livestock producers and manure applicators should contact their local Conservation District MAEAP technician for help in developing a manure management plan that takes into account a manure-spreading plan, sensitive-area field maps and alternatives to spreading, if necessary. Another great resource for making manure application decisions is MDARD’s Right to Farm Generally Accepted Agricultural Management Practices (GAAMPs) specific to manure management and utilization.
The MSU EnviroImpact Tool is currently under development and will be available soon. Livestock producers, manure applicators and others are encouraged to preview the tool and provide feedback. If you are interested in accessing the tool and providing feedback, please contact either Shelby Burlew, MSU Extension, at bollwah1@anr.msu.edu or Jason Piwarski, MSU Institute of Water Research, at piwarsk1@msu.edu for access to the tool’s website.
Editor’s Note: Shelby Burlew is an environmental quality educator for Michigan State University Extension.







